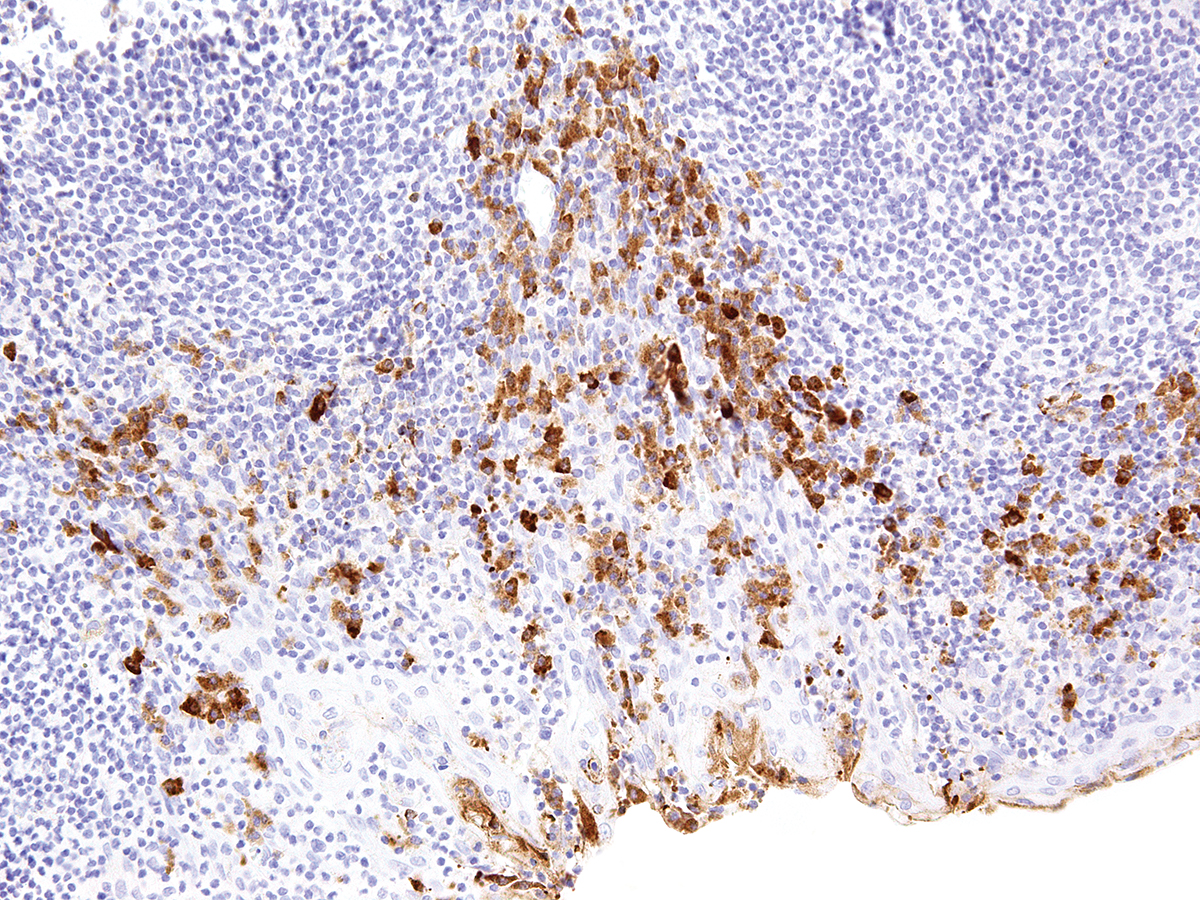
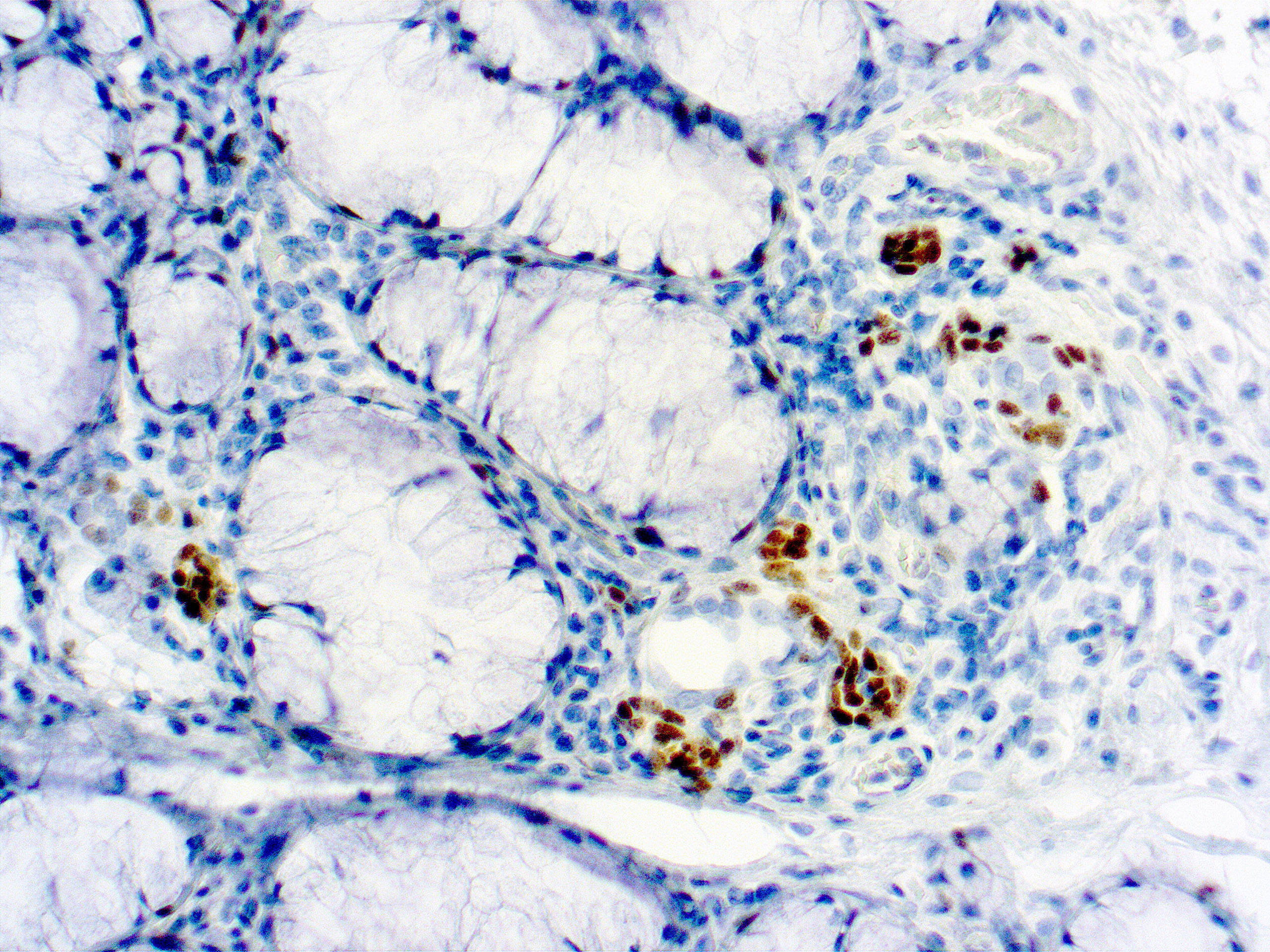
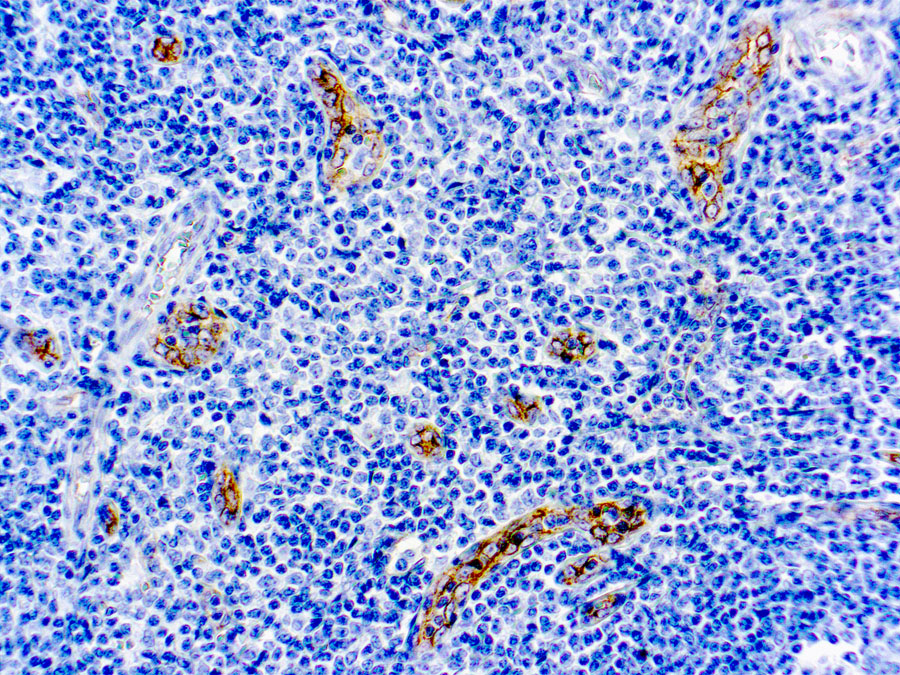
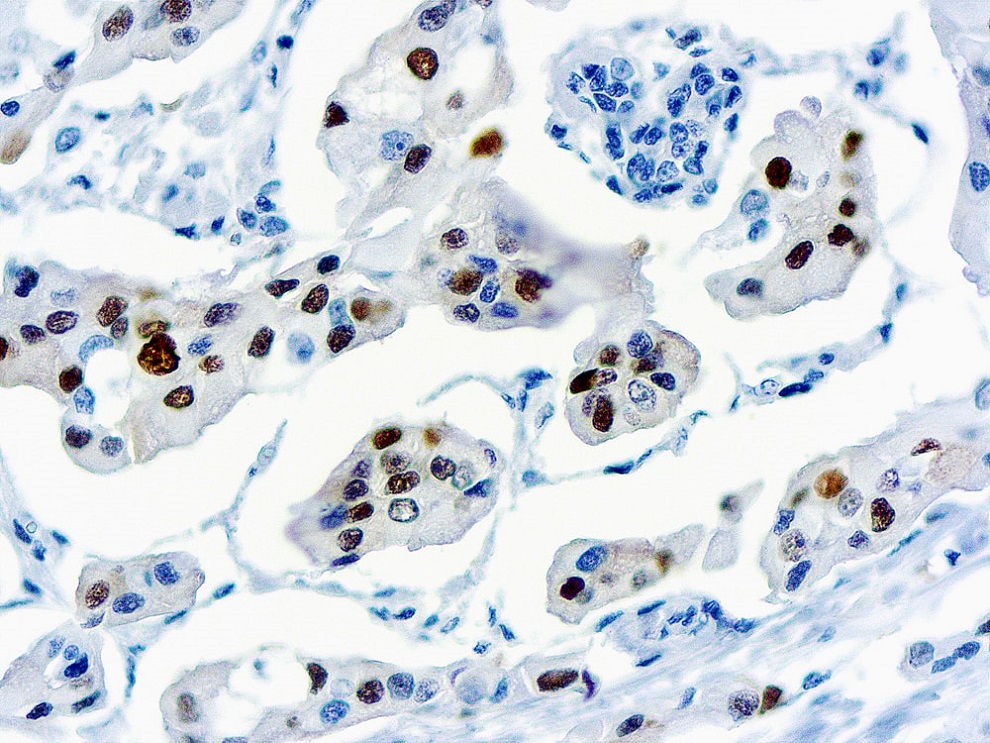
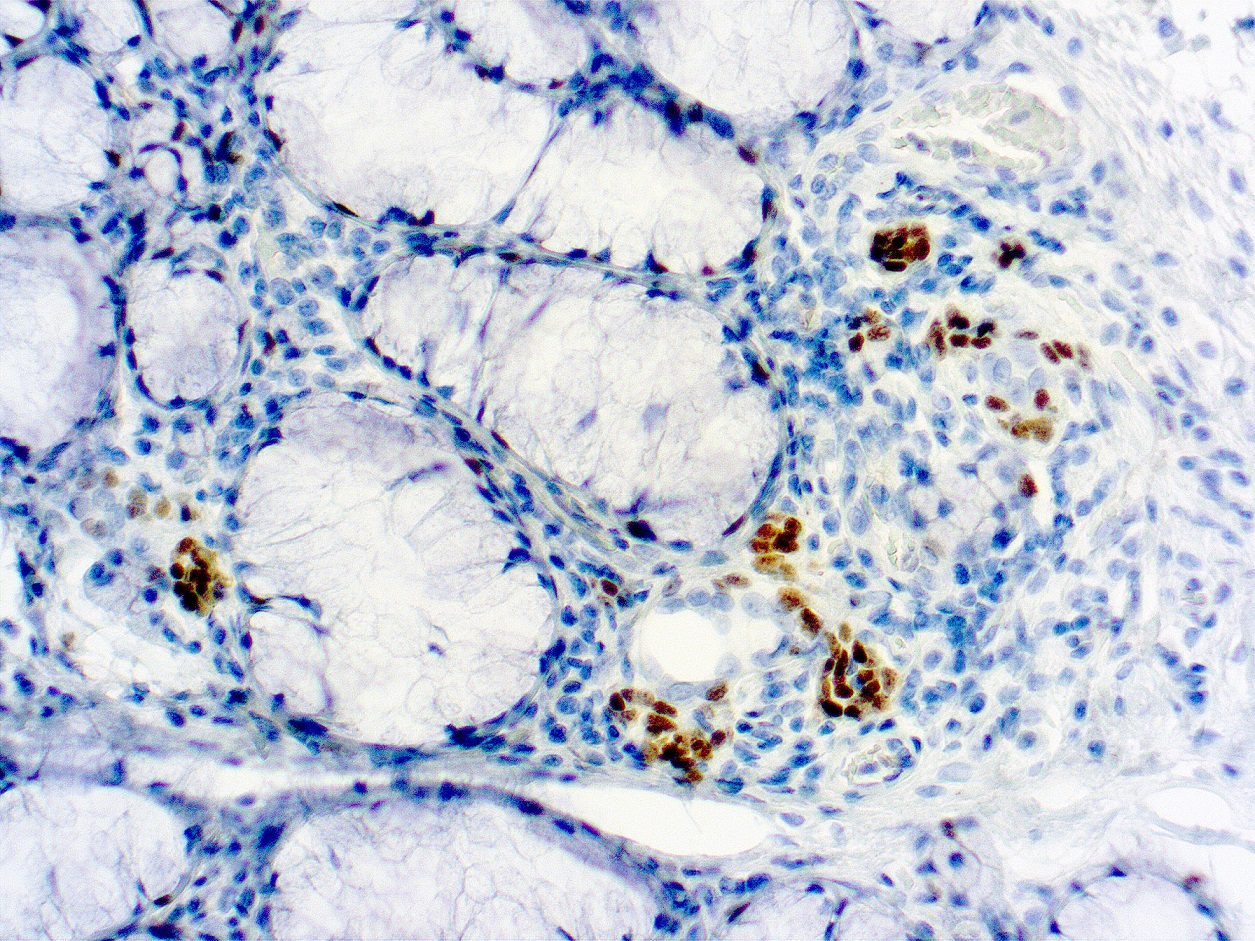
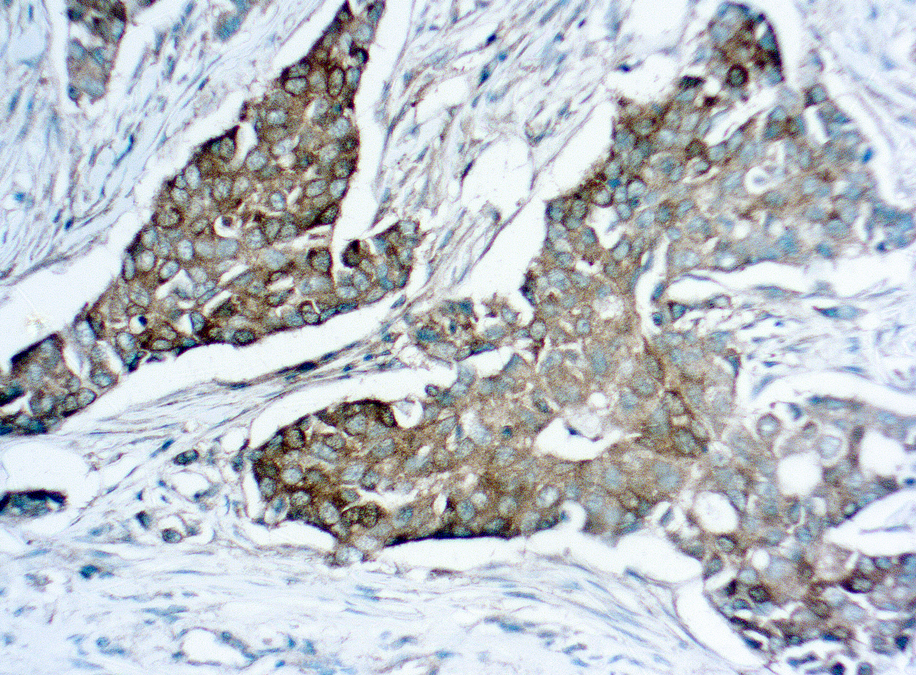
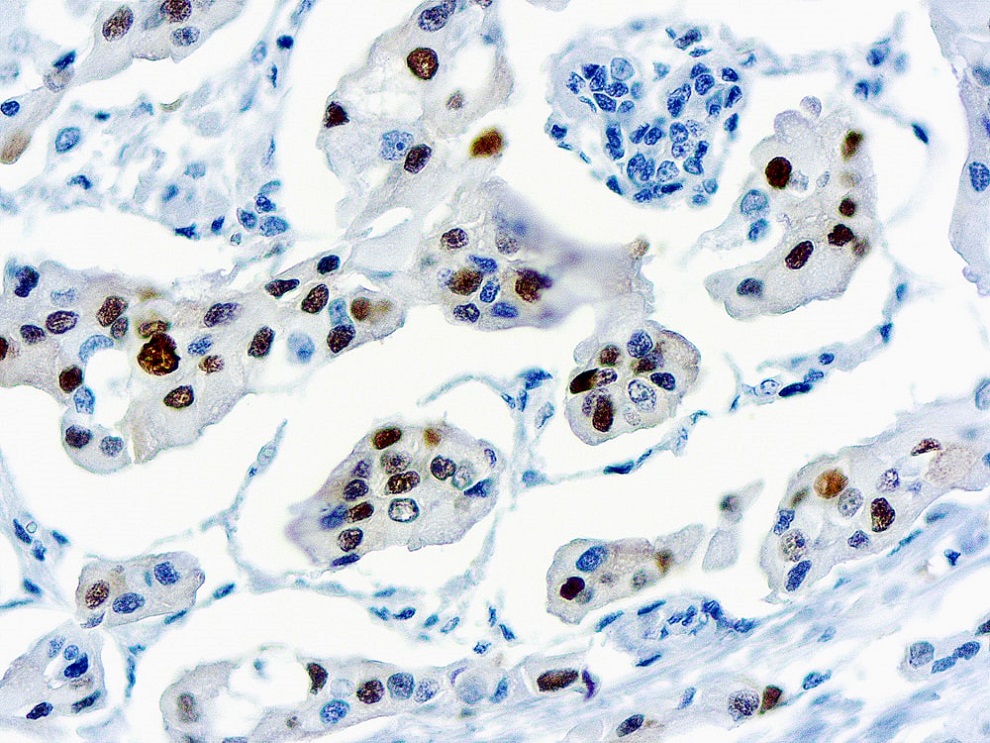
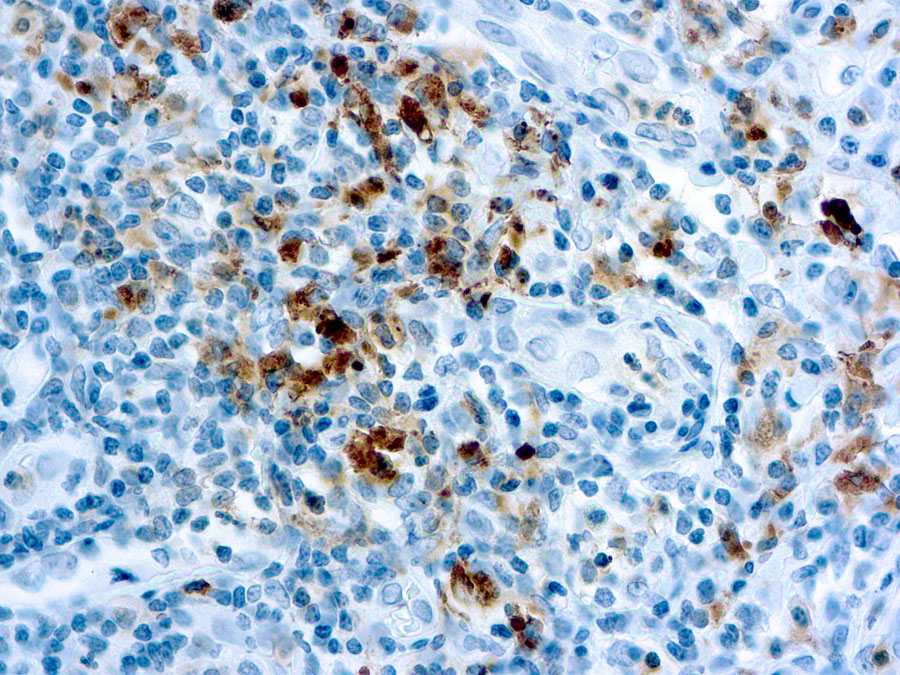
CTLA-4 - Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 3
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) is a receptor on T Helper cells that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulator of immune responses. Mutations in CTLA-4 are associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Graves’ disease, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), celiac disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, thyroid-associated orbitopathy, multiple sclerosis, and other autoimmune diseases. The spliced variant of CTLA-4 in SLE is present in the patient’s serum. Haploinsufficiency of CTLA-4 causes the immune system disorder known as CTLA-4 deficiency or CHAI disease (CTLA4 haploinsufficiency with autoimmune infiltration).
0,1 ml
| Clone | IHC004 |
| Application | IHC |
| Host | Mouse |
La documentación estará disponible en breve, mientras tanto, puede contactarnos por correo electrónico a specialist@histoline.com